Mastering AWSand Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform/OpenTofu opens up countless possibilities in the world of modern cloud computing. Whether you're looking to progress in your career, enhance cloud operations, or push the boundaries with innovative technologies, cloud expertise is a crucial asset in today’s tech-focused landscape.
Table of Contents
- Motivation: Where Do Cloud Skills Help Us?
- What are Lambda, IAM Role/Policy, API Gateway?
- Hands-on Sample
- Steps
Motivation: Where Do Cloud Skills Help Us?
Cloud expertise extends beyond IT professionals, it's valuable across various domains:
- DevOps & SRE Roles: Automating infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring applications.
- Software Development: Deploying, scaling, and managing cloud-native applications.
- Data Science & AI/ML: Leveraging cloud-based data lakes, analytics, and AI services.
- Cybersecurity & Compliance: Securing cloud resources and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Enterprise IT & Digital Transformation: Driving business innovation with cloud-first strategies.
- Freelancers & Entrepreneurs: Hosting applications, automating deployments, and reducing operational costs.
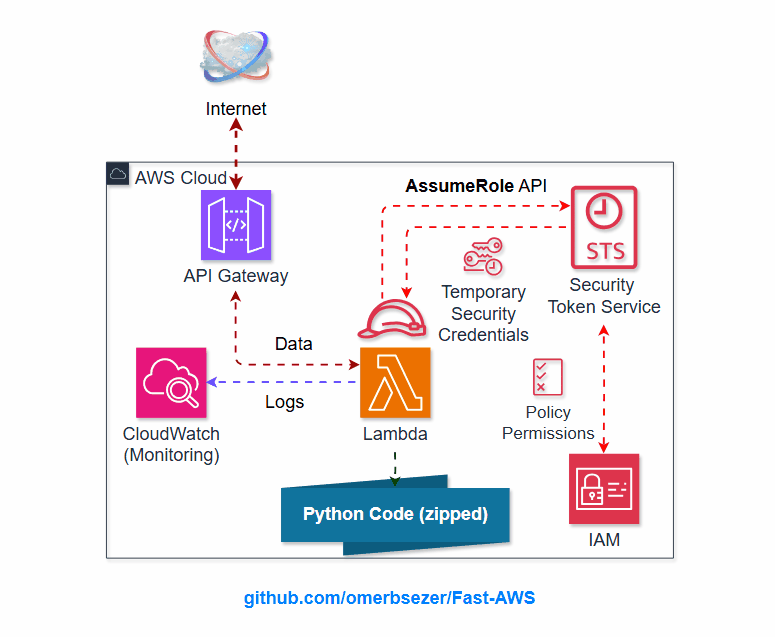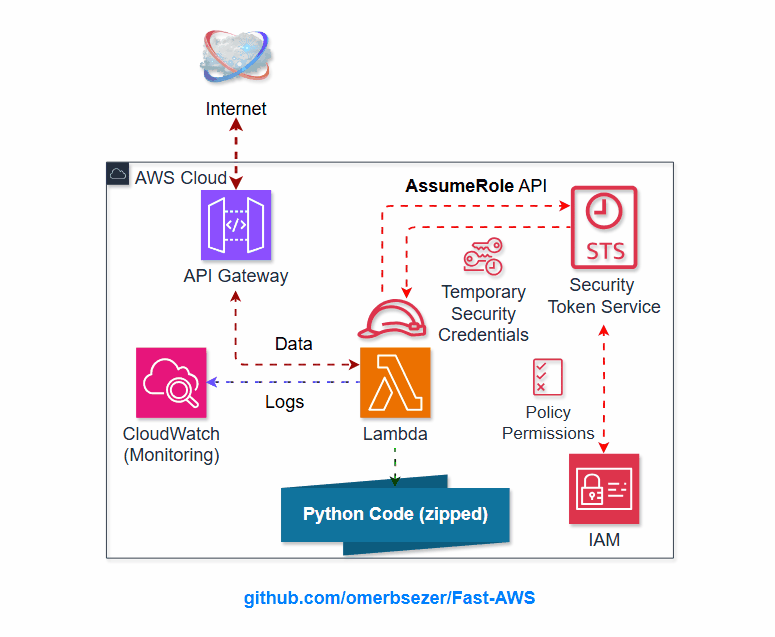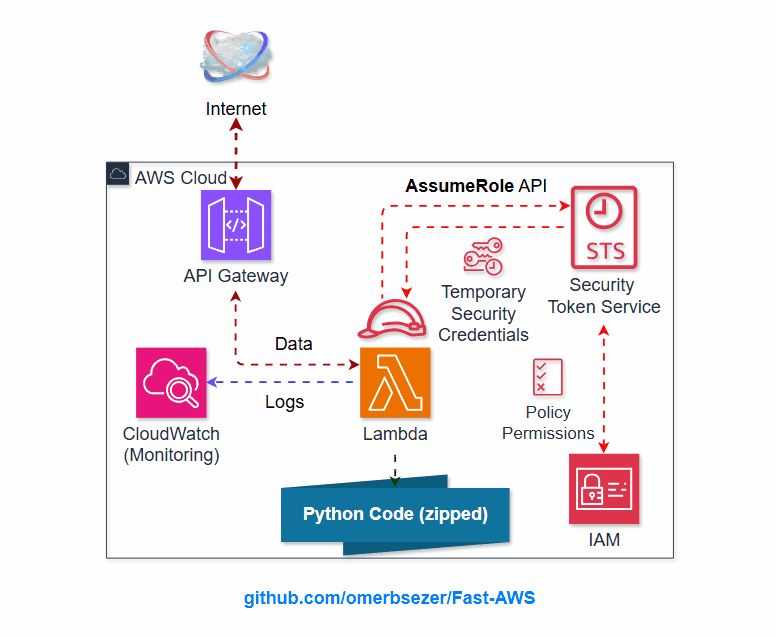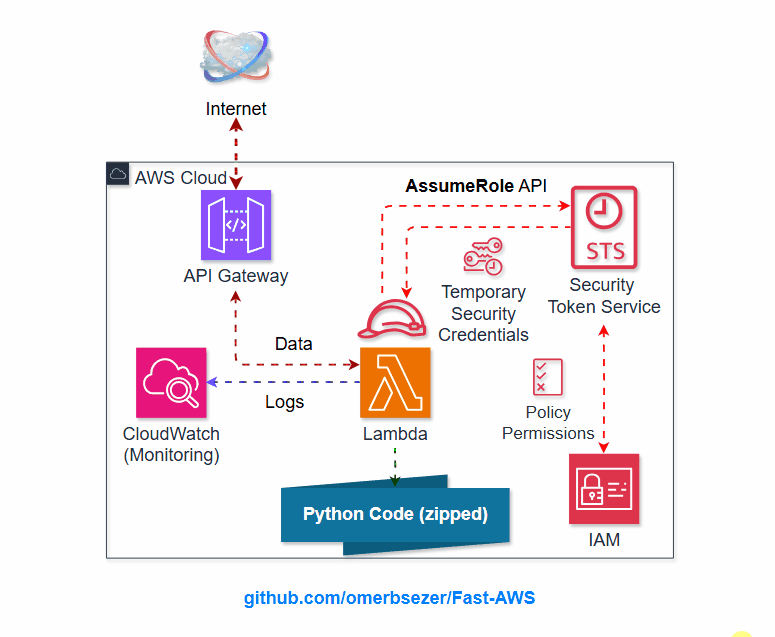
What are Lambda, IAM Role/Policy, API Gateway?
AWS Lambda: A
serverless compute servicethat allows you to run code in response to events without provisioning or managing servers.IAM Role: A
set of permissionsthat define whatactions an entity(like a Lambda function or EC2 instance) canperformin AWS.IAM Policy: A
documentthatdefines specific permissions for users, groups, or roles, controlling what actions are allowed or deniedon AWS resources.sts:AssumeRole: An action in AWS Security Token Service (STS) that
allows one entity to temporarily assumea different role and inherit its permissions.API Gateway: A fully managed service that
enables you to create, publish, and manage APIsfor accessing backend services, such as Lambda functions, securely and at scale.Lambda Permission: Grants API Gateway
the permission to invoke a Lambda function, enabling the API to trigger Lambda for backend processing.
Hands-on Sample
This sample shows:
- how to create Lambda function with Python code,
- how to create Lambda Role, Policy, Policy-Role attachment, Lambda API-gateway permission, uploading code,
- how to create API-gateway resource and method definition, Lambda-API-gateway connection, deploying API-gateway,
- details on AWS Lambda, API-Gateway, IAM
There are 3 main parts:
- lambda.tf: It includes lambda function, lambda role, policy, policy-role attachment, lambda api gateway permission, zipping code
- api-gateway.tf: It includes api-gateway resource and method definition, lambda - api gateway connection, deploying api gateway, api-gateway deployment URL as output
- code/main.py: It includes basic lambda handler with basic HTML code, and REST API response.
Steps
- Create lambda.tf:
- Terraform Configuration: Specifies the AWS provider version and Terraform version.
- IAM Role and Policy: Creates an IAM role for the Lambda function and attaches a policy that allows the Lambda function to write logs to CloudWatch.
- Zipping Lambda Code: Prepares the Python code by zipping it into a format that Lambda can execute.
- Lambda Function: Creates a Lambda function using the specified IAM role, , and runtime.
- API Gateway Integration: Grants API Gateway permission to invoke the Lambda function.
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.16"
}
}
required_version = ">= 1.2.0"
}
# Create IAM Role for lambda
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_role" {
name = "aws_lambda_role"
assume_role_policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Principal": {
"Service": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": ""
}
]
}
EOF
}
# IAM policy for the lambda
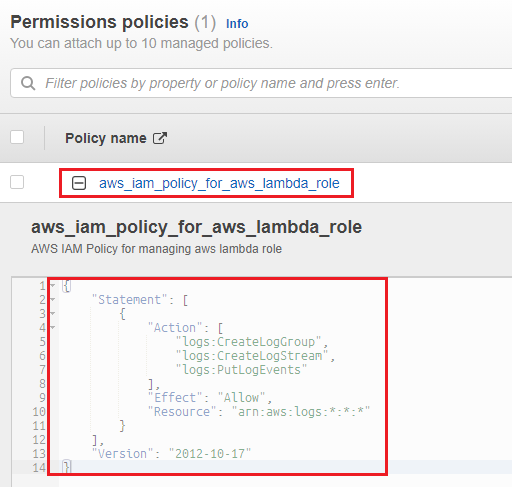
resource "aws_iam_policy" "iam_policy_for_lambda" {
name = "aws_iam_policy_for_aws_lambda_role"
path = "/"
description = "AWS IAM Policy for managing aws lambda role"
policy = <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*",
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}
EOF
}
# Role - Policy Attachment
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "attach_iam_policy_to_iam_role" {
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.iam_policy_for_lambda.arn
}
# Zipping the , lambda wants the as zip file
data "archive_file" "zip_the_python_" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = "${path.module}//"
output_path = "${path.module}//main.zip"
}
# Lambda Function, in terraform ${path.module} is the current directory.
resource "aws_lambda_function" "lambda_function" {
filename = "${path.module}//main.zip"
function_name = "Lambda-Function"
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_role.arn
handler = "main.lambda_handler"
runtime = "python3.8"
depends_on = [aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.attach_iam_policy_to_iam_role]
}
# With Lambda permission, API Gateway can invoke Lambda
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "apigw" {
statement_id = "AllowAPIGatewayInvoke"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
# The "/*/*" portion grants access from any method on any resource within the API Gateway REST API.
source_arn = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
- Create api-gateway.tf:
- Proxy Usage: The {proxy+} path is used to dynamically route all requests to the Lambda function, eliminating the need to define individual paths and methods.
- Flexibility: The ANY method allows all HTTP methods, making the API flexible.
- AWS_PROXY Integration: Simplifies the interaction between API Gateway and Lambda by passing the entire request data to Lambda, allowing it to process dynamically.
# Create API Gateway with Rest API type
resource "aws_api_gateway_rest_api" "example" {
name = "Serverless"
description = "Serverless Application using Terraform"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_resource" "proxy" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
parent_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.root_resource_id
path_part = "{proxy+}" # with proxy, this resource will match any request path
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "proxy" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_resource.proxy.id
http_method = "ANY" # with ANY, it allows any request method to be used, all incoming requests will match this resource
authorization = "NONE"
}
# API Gateway - Lambda Connection
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "lambda" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_method.proxy.resource_id
http_method = aws_api_gateway_method.proxy.http_method
integration_http_method = "POST"
type = "AWS_PROXY" # With AWS_PROXY, it causes API gateway to call into the API of another AWS service
uri = aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.invoke_arn
}
# The proxy resource cannot match an empty path at the root of the API.
# To handle that, a similar configuration must be applied to the root resource that is built in to the REST API object
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "proxy_root" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.root_resource_id
http_method = "ANY"
authorization = "NONE"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "lambda_root" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_method.proxy_root.resource_id
http_method = aws_api_gateway_method.proxy_root.http_method
integration_http_method = "POST"
type = "AWS_PROXY" # With AWS_PROXY, it causes API gateway to call into the API of another AWS service
uri = aws_lambda_function.lambda_function.invoke_arn
}
# Deploy API Gateway
resource "aws_api_gateway_deployment" "example" {
depends_on = [
aws_api_gateway_integration.lambda,
aws_api_gateway_integration.lambda_root,
]
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.example.id
stage_name = "test"
}
# Output to the URL
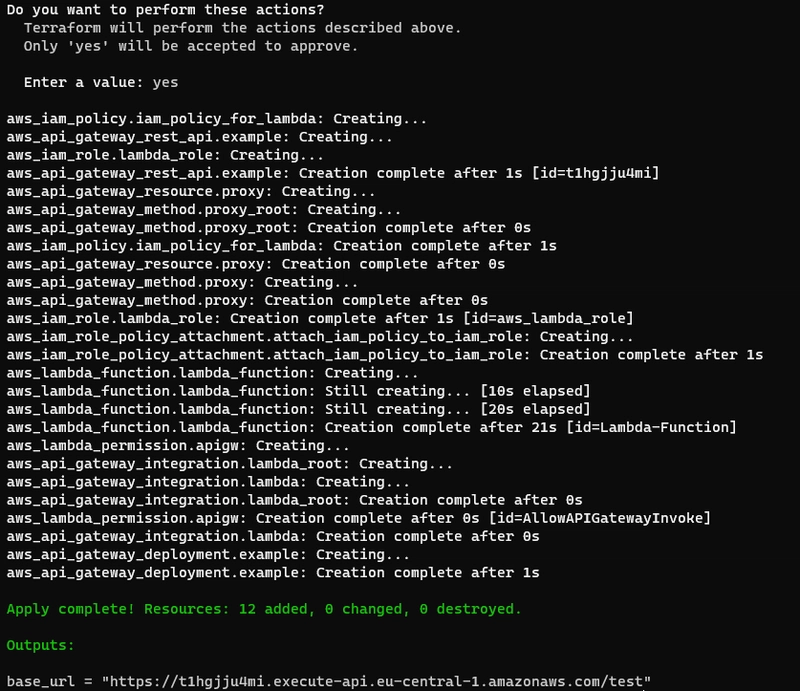
output "base_url" {
value = aws_api_gateway_deployment.example.invoke_url
}
- Create main.py under code directory:
def lambda_handler(event, context):
content = """
<html>
<h1> Hello Website running on Lambda! Deployed via Terraform </h1>
</html>
"""
response ={
"statusCode": 200,
"body": content,
"headers": {"Content-Type": "text/html",},
}
return response
- Run init, validate command:
terraform init
terraform validate
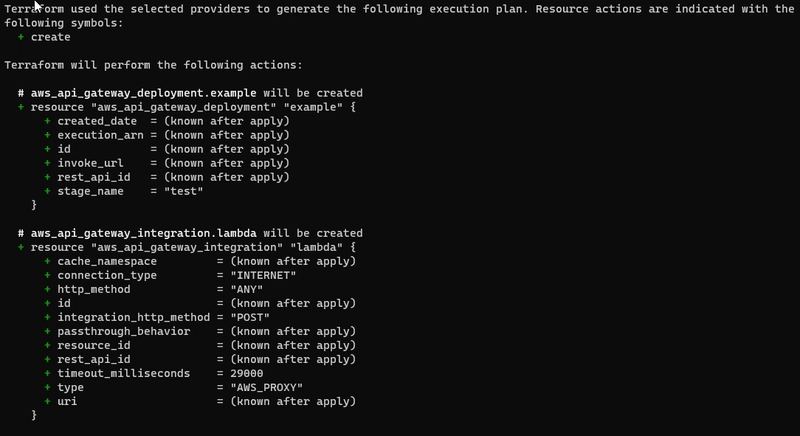
- Run plan, apply command:
terraform plan # for dry-run
terraform apply
- On AWS Lambda:
- Create a test by clicking "Test" for lambda function:
- Status code 200, OK is returned successfully:
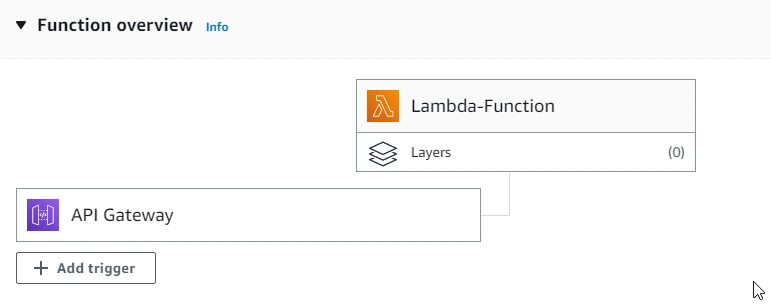
- Execution Role is created, seen on Lambda
- Role on IAM:
- Policy on IAM:
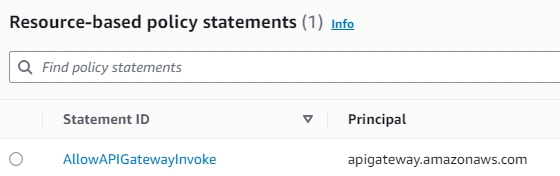
- On AWS Lambda: With Lambda permission, API Gateway can invoke Lambda
- Lambda is triggered by API-Gateway:
- On AWS API-Gateway:
- By clicking "Test" to test api-gateway
- HTML page that runs on Lambda Function using API-Gateway can be reached. With API-Gateway, lambda function gets DNS and traffic from internet comes to the Lambda function.
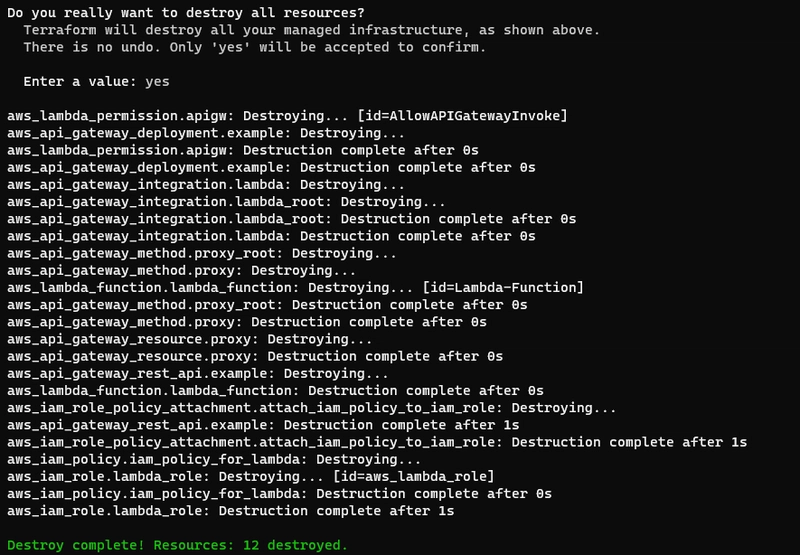
- Run destroy command:
terraform destroy
- On AWS Lambda, function is deleted
Conclusion
In this post, we mentioned:
- why should we learn Cloud/AWS, IaC/Terraform,
- how to provision AWS Lambda, API GW, IAM Role and Policy, Assume Role,
- how to connect Lambda, API GW,
- how to configure API GW with Terraform,
If you found the tutorial interesting, I’d love to hear your thoughts in the blog post comments. Feel free to share your reactions or leave a comment. I truly value your input and engagement 😉
For other posts 👉 https://dev.to/omerberatsezer 🧐
Let's Discuss! 🤝
- Why should we learn Lambda and/or API Gateway?
- What are your popular Cloud/AWS services?
















Top comments (1)
My popular cloud service on AWS is Bedrock nowadays. I use Bedrock to run different models (Llama 3.1 405B, Llama3.3 70B, Nova, etc.). It can also be used Bedrock with Lambda and API Gateway to build real-time GenAI apps like chatbots. API Gateway handles requests, Lambda calls Bedrock, and IAM secures it all for fully serverless and scalable.