1857. Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph
Difficulty: Hard
Topics: Hash Table, Dynamic Programming, Graph, Topological Sort, Memoization, Counting
There is a directed graph of n colored nodes and m edges. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are given a string colors where colors[i] is a lowercase English letter representing the color of the ith node in this graph (0-indexed). You are also given a 2D array edges where edges[j] = [aj, bj] indicates that there is a directed edge from node aj to node bj.
A valid path in the graph is a sequence of nodes x1 -> x2 -> x3 -> ... -> xk such that there is a directed edge from xi to xi+1 for every 1 <= i < k. The color value of the path is the number of nodes that are colored the most frequently occurring color along that path.
Return the largest color value of any valid path in the given graph, or -1 if the graph contains a cycle.
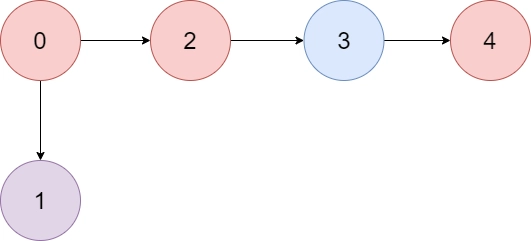
Example 1:
- Input: colors = "abaca", edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[3,4]]
- Output: 3
-
Explanation: The path 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 contains 3 nodes that are colored
"a" (red in the above image).
Example 2:
- Input: colors = "a", edges = [[0,0]]
- Output: -1
- Explanation: There is a cycle from 0 to 0.
Constraints:
n == colors.lengthm == edges.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= m <= 105-
colorsconsists of lowercase English letters. 0 <= aj, bj < n
Hint:
- Use topological sort.
- let dp[u][c] := the maximum count of vertices with color c of any path starting from vertex u. (by JerryJin2905)
Solution:
We need to determine the largest color value in a directed graph, considering possible cycles. If the graph contains a cycle, we return -1. Otherwise, we compute the maximum color value using dynamic programming combined with topological sorting.
Approach
- Cycle Detection and Topological Sort: Use Kahn's algorithm to perform a topological sort. If the number of processed nodes is less than the total nodes, the graph contains a cycle, and we return -1.
-
Dynamic Programming (DP): For each node processed in topological order, maintain a DP array where
dp[u][c]represents the maximum count of colorcin any path ending at nodeu. - Reverse Adjacency List: Track predecessors for each node to efficiently update DP values based on incoming edges.
- Color Count Update: For each node, initialize its DP array with its own color count. Then, update the DP values by considering all paths from predecessors, incrementing the count if the current node's color matches.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 1857. Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph
<?php
/**
* @param String $colors
* @param Integer[][] $edges
* @return Integer
*/
function largestPathValue($colors, $edges) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
$colors = "abaca";
$edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[3,4]];
echo largestPathValue($colors, $edges); // Output: 3
$colors = "a";
$edges = [[0,0]];
echo largestPathValue($colors, $edges); // Output: -1
?>
Explanation:
- Topological Sorting: Using Kahn's algorithm, we process nodes in a topological order. This ensures that each node is processed only after all its predecessors have been processed, which is crucial for correctly updating DP values.
- Cycle Detection: If the topological sort processes fewer nodes than the total nodes, a cycle exists, and we return -1.
- DP Initialization: Each node starts with a DP array initialized to 0 except for its own color, which is set to 1.
- Updating DP Values: For each node, we update its DP array by considering all incoming edges (predecessors). For each predecessor, we check all color counts and update the current node's DP values to reflect the maximum possible counts from all paths ending at the current node.
- Result Calculation: The maximum value in the DP array for each node is tracked to determine the largest color value in any valid path.
This approach efficiently combines topological sorting and dynamic programming to solve the problem in linear time relative to the number of edges and nodes, making it suitable for large input sizes.
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks 😍. Your support would mean a lot to me!
If you want more helpful content like this, feel free to follow me:





Top comments (0)