Introduction
When building relational databases in Java, understanding how to map relationships between entities is crucial. One of the most common relationships is One-to-Many mapping. In this guide, we’ll break it down in a way that’s super easy to grasp and fun to learn! 🤩
By the end of this article, you’ll learn:
- What One-to-Many mapping is.
- How to implement it using Spring Boot, JPA, and Hibernate.
- The different ways to set up the relationship.
- Real-world use cases to apply in your projects.
Let’s get started! 🚀
What is One-to-Many Mapping?
A One-to-Many relationship means that one entity is related to multiple entities.
Real-World Examples:
- A blog post can have multiple comments.
- A customer can have multiple orders.
- A department can have multiple employees.
In database terms, this means the primary key of one table is referenced as a foreign key in another table.
JPA makes this easy using the @OneToMany annotation. Let’s see how to implement it! 🔥
Implementing One-to-Many Mapping in Spring Boot
1️⃣ One-to-Many Using a Foreign Key (Recommended ✅)
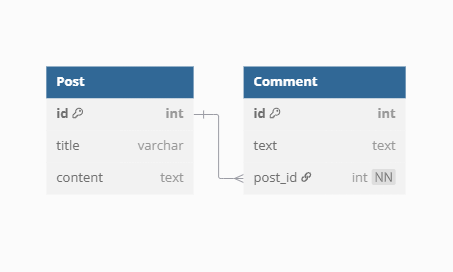
The most common approach is to have a foreign key in the child table referencing the parent table’s primary key.
📌 Step 1: Create the Post Entity
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import java.util.List;
@Entity
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String content;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post", cascade = CascadeType.ALL, orphanRemoval = true)
private List<Comment> comments;
// Getters and Setters
}
📌 Step 2: Create the Comment Entity
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
public class Comment {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String text;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "post_id", nullable = false)
private Post post;
// Getters and Setters
}
🔹 Explanation:
- The
Postentity has aList<Comment>to represent multiple comments. -
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post")inPosttells JPA thatCommentowns the relationship. - The
Commententity has a@ManyToOneannotation with a@JoinColumn(name = "post_id")to store the foreign key.
💡 Tip: The cascade = CascadeType.ALL ensures that when a Post is deleted, its comments are also removed. orphanRemoval = true helps keep the database clean!
2️⃣ One-to-Many Using a Join Table 🏛️
Sometimes, instead of a foreign key in the child table, you may want to use a third table to manage the relationship.
📌 Modify the Post Entity
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinTable(
name = "post_comments",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "post_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "comment_id")
)
private List<Comment> comments;
🔹 This approach creates a post_comments table that holds post_id and comment_id as foreign keys, linking the two tables.
When to Use One-to-Many Mapping?
One-to-Many relationships are useful when:
✅ An entity owns multiple child entities (e.g., a blog post with comments).
✅ You need to maintain data integrity (e.g., orders belonging to a customer).
✅ You want to avoid data duplication while keeping a structured relationship.
Conclusion 🎯
In this article, we explored:
- What One-to-Many mapping is.
- How to implement it in Spring Boot using JPA.
- Different approaches (foreign key vs. join table).
- When to use it in real-world applications.
One-to-Many mapping is one of the most commonly used relationships in database design. Mastering it will make you a better backend developer! 🚀
💬 Got questions? Let me know in the comments! Happy coding! 😃



Top comments (0)