Two weeks ago, I released the first public version of Human Regex, and I’m thrilled to share that it now leverages TypeScript’s magic typing to take regex building to the next level! This update not only brings a host of bug fixes but also introduces a smarter, safer API for crafting regular expressions. Thanks to two new contributors—one of whom contributed the powerful magic typing—Human Regex has already gained 900+ downloads.
Why is Human Regex better than traditional regex in JS/TS?
- English-like Syntax: Build regex patterns in a readable, chainable syntax that feels like natural language.
- Magic Typing: Enforces valid regex construction at compile time, catching mistakes early and making your code safer.
Want to Learn More?
- 🔎 Missed the gist, check out my previous blog post.
- 📘 Explore the latest tutorial: Dive deeper into using Human Regex in your JS/TS projects by completing this blog post.
Getting Started
Installation:
Start by installing Human Regex in your project:
npm install human-regex
Then import the library in your TypeScript code:
import { createRegex } from "human-regex";
Simple Examples:
Basic Literal Match:
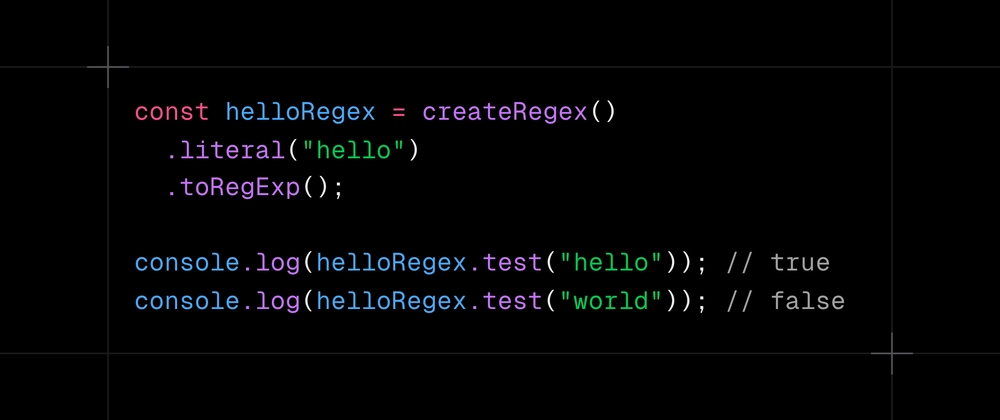
Match the exact word "hello" without worrying about special character escaping.
const helloRegex = createRegex()
.literal("hello")
.toRegExp();
console.log(helloRegex.test("hello")); // true
console.log(helloRegex.test("world")); // false
Digit Matching:
Create a regex that matches only digits.
const digitRegex = createRegex()
.digit()
.toRegExp();
console.log(digitRegex.test("5")); // true
console.log(digitRegex.test("a")); // false
Using the OR Operator:
Match one of multiple options using the .or() method.
const animalRegex = createRegex()
.literal("cat")
.or()
.literal("dog")
.toRegExp();
console.log(animalRegex.test("cat")); // true
console.log(animalRegex.test("dog")); // true
console.log(animalRegex.test("bat")); // false
Whitespace Matching:
Check if a string contains a whitespace character.
const whitespaceRegex = createRegex()
.whitespace()
.toRegExp();
console.log(whitespaceRegex.test(" ")); // true
console.log(whitespaceRegex.test("a")); // false
Escaping Special Characters:
The .literal() method automatically escapes special characters for you.
const specialCharsRegex = createRegex()
.literal(".*+?^${}()|[]\\")
.toRegExp();
console.log(specialCharsRegex.test(".*+?^${}()|[]\\")); // true
Protocol Validation:
Build a regex to check for a valid HTTP/HTTPS protocol.
const protocolRegex = createRegex()
.protocol()
.toRegExp();
console.log(protocolRegex.test("http://")); // true
console.log(protocolRegex.test("https://")); // true
console.log(protocolRegex.test("ftp://")); // false
Named Capture Group:
Extract a substring using a named capture group.
const namedGroupRegex = createRegex()
.startNamedGroup("digits")
.digit()
.oneOrMore()
.endGroup()
.literal("-end")
.toRegExp();
const match = "12345-end".match(namedGroupRegex);
if (match?.groups) {
console.log(match.groups.digits); // "12345"
}
Matching Exactly Three Digits:
Ensure a string contains exactly three digits.
const threeDigitsRegex = createRegex()
.startAnchor()
.digit()
.exactly(3)
.endAnchor()
.toRegExp();
console.log(threeDigitsRegex.test("123")); // true
console.log(threeDigitsRegex.test("12")); // false
console.log(threeDigitsRegex.test("1234")); // false
Error Handling Examples:
Human Regex includes smart typing and runtime checks to help you catch mistakes early. Here are two examples that intentionally trigger errors:
Error Example 1: Using .lazy() on an Empty Pattern
try {
// No quantifier exists, so calling .lazy() throws an error.
createRegex().lazy();
} catch (e) {
console.error(e.message); // Expected output: "No quantifier to make lazy"
}
Error Example 2: Invalid Unicode Letter Variant
try {
// "x" is not a valid Unicode letter variant.
createRegex().unicodeChar("x" as any);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e.message); // Expected output: "Invalid Unicode letter variant: x"
}
Conclusion
Human Regex transforms the complexity of traditional regex into a series of intuitive method calls. Whether you’re matching a simple literal, testing digits, or combining multiple methods for complex patterns, the library offers a clear and maintainable approach. Its robust type system and runtime checks help prevent common mistakes, making your code safer and easier to debug.
Have you explored Human Regex in your projects? I’d love to hear your experiences or see your examples in the comments below!
You can also contribute by:
⭐ Starring the GitHub repo to help others discover it
🐞 Reporting bugs or requesting features
💡 Contributing code or documentation
Happy coding!




Top comments (0)