You're the new Junior Sysadmin at a small but busy tech startup. It's your first week on the job, and you've just been asked to monitor, troubleshoot, and control running processes on the company's servers.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to monitor and manage Linux processes through hands-on examples. We’ll create dummy processes, explore real-time tools, and learn how to gently—or forcefully—handle misbehaving tasks.
📚 Table of Contents
- 🔧 Setting Up Your Practice Environment
- 📊 Monitoring Processes in Real-Time
- 🔍 Viewing Detailed Process Info
- 🧼 Cleaning Up Processes
- 🎯 Managing Background Jobs
- ⚙️ Changing Process Priority
- 🧪 Bonus Tools to Try
- 🧠 Summary: Command Cheat Sheet
🔧 Setting Up Your Practice Environment
Simulate real-world tasks by launching test processes:
Create a working directory:
mkdir ~/process-lab && cd ~/process-lab
Create an infinite loop script:
echo -e '#!/bin/bash
while true; do echo "Working..."; sleep 5; done' > worker.sh
🔍 Breakdown of What It Does:
echo -e
echo: Prints text to the terminal or into a file.
-e: Enables interpretation of backslash escapes (like \n for newline).
#!/bin/bash
This is a shebang. It tells the system to execute the script using the Bash shell.
while true; do echo "Working..."; sleep 5; done
This is an infinite loop:
while true; means “loop forever.”
echo "Working..."prints the message to the screen.
sleep 5pauses for 5 seconds between each print to avoid spamming.
donemarks the end of the loop block.
worker.sh
Redirects the whole output into a file called worker.sh.If the file exists, it will be overwritten.
Make it executable:
chmod +x worker.sh
Note: Review the kill cmd before proceeding, you'll thank yourself in a few moments.
Run it in the background:
./worker.sh &
Note: Record the process ID (PID)
By now you are annoyed because
Working...continues to print to screen. But we can discard the output with/dev/nullor redirect it to a log by editing the script. Example here:
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo "Working..." >> ~/process-lab/worker.log
sleep 5
done
I don't need the output for this example, so I will discard them.
#!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo "Working..." >> /dev/null
sleep 5
done
Create a CPU-intensive process:
yes > /dev/null &
-
yesprints "y" repeatedly;/dev/nulldiscards the output. This simulates high CPU usage.
📊 Monitoring Processes in Real-Time
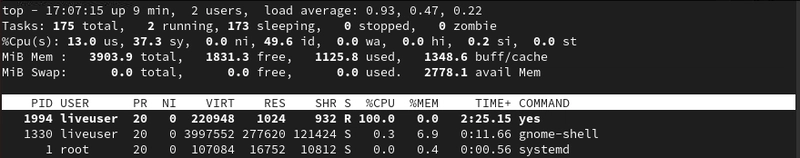
top
top
- What it does: Shows real-time info on CPU, memory, and processes.
-
Navigation tips: Use
qto quit,Pto sort by CPU, andMto sort by memory.
htop
htop
-
What it does: A friendlier alternative to
topwith color and interactivity. -
Useful features: Scrollable list, search with
/, kill withF9. - Install it:
sudo dnf install htop
Note: If htop is not available by default, try these additional steps:
Enable EPEL repository:
sudo dnf install epel-release
Update your package index (optional):
sudo dnf update
🔍 Viewing Detailed Process Info
ps aux
ps aux | grep worker.sh
-
ps: Shows process snapshot. -
a: Show processes from all users. -
u: Display in user-oriented format. -
x: Include background and non-terminal processes. -
grep worker.sh: Filter to find our script.
pstree -p
pstree -p
- What it does: Displays processes as a tree with PIDs.
- Great for spotting parent-child relationships.
🧼 Cleaning Up Processes
kill <PID>
kill 1234
-
What it does: Sends signal (default:
SIGTERM) to request graceful stop.
kill -9 <PID>
kill -9 1234
-
-9=SIGKILL: Forces termination without cleanup. - Use only if normal kill doesn't work.
pkill <name>
pkill worker.sh
- Ends all processes matching the name
worker.sh. - Safer than hunting for PIDs manually.
🎯 Managing Background Jobs
Background a command with &
sleep 60 &
- Launches
sleepas a background job.
Check jobs
jobs
- Shows background jobs for current session.
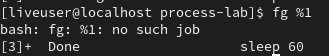
Bring job to foreground
fg %1
-
%1: Refers to job number 1.
Send to background again
bg %1
⚙️ Changing Process Priority
nice
nice -n 10 ./worker.sh &
-
-n 10: Starts the process with a niceness of 10 (lower priority). - Range: -20 (high priority) to 19 (low priority).
renice
renice -n 5 -p 1234
- Changes priority of process
1234to niceness5. - Requires root to decrease niceness (i.e., increase priority).
🧪 Bonus Tools to Try
systemctl status <service>
systemctl status sshd
- Checks if the
sshdservice is running. - Useful for managing system-level daemons.
watch
watch -n 1 ps aux | grep worker
- Repeats a command every second.
- Great for monitoring state changes.
strace
strace -p <PID>
- Traces system calls for a process.
- Advanced troubleshooting tool.
🧠 Summary: Command Cheat Sheet
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
top, htop
|
Real-time CPU/memory monitoring |
ps aux |
List all active processes |
kill <PID> |
Gracefully stop a process |
kill -9 <PID> |
Forcefully terminate a process |
pkill <name> |
Kill process by name |
jobs, fg, bg
|
Manage shell background jobs |
nice, renice
|
Set or change process priority |
pstree |
View process hierarchy |
watch, strace
|
Monitor and trace process behavior |
✅ Wrap Up
Linux process management isn't just about knowing commands—it's about understanding how and when to use them. Set up a test environment, try each command, and you'll gain confidence in keeping your systems stable and responsive.
Happy sysadmin-ing!








Top comments (1)
Some comments may only be visible to logged-in visitors. Sign in to view all comments.