AWS CloudFormation is a powerful tool that allows you to define and provision AWS infrastructure as code. In this blog post, I’ll walk you through setting up a complete infrastructure using CloudFormation, including a VPC, Subnet, Route Table, Security Group, and EC2 Instance. I’ll also demonstrate how CloudFormation detects drift when resources are modified outside of the stack.
What I’ll Build
Using CloudFormation, we’ll create:
- A VPC with DNS support enabled.
- A Subnet within the VPC.
- An Internet Gateway and a Route Table for public access.
- A Security Group to allow SSH and HTTP traffic.
- An EC2 Instance running Amazon Linux 2.
- Drift detection to monitor changes made outside of CloudFormation.
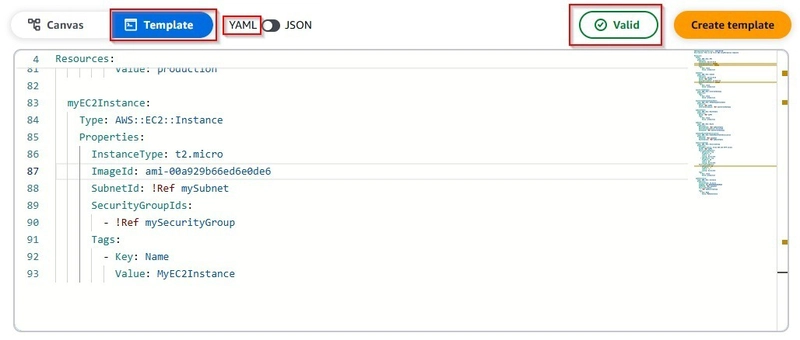
CloudFormation Template
Here’s the YAML template used to define the infrastructure:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: This is my first AWS CloudFormation template
Resources:
myVPC:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPC
Properties:
CidrBlock: 38.0.0.0/16
EnableDnsSupport: 'true'
EnableDnsHostnames: 'true'
Tags:
- Key: stack
Value: production
mySubnet:
Type: AWS::EC2::Subnet
Properties:
CidrBlock: 38.0.0.0/16
VpcId: !Ref myVPC
AvailabilityZone: us-east-1a
MapPublicIpOnLaunch: 'true'
Tags:
- Key: stack
Value: production
myInternetGateway:
Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway
Properties:
Tags:
- Key: stack
Value: production
myInternetGatewayAttachment:
Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref myVPC
InternetGatewayId: !Ref myInternetGateway
myRouteTable:
Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable
Properties:
VpcId: !Ref myVPC
Tags:
- Key: stack
Value: production
myRoute:
Type: AWS::EC2::Route
Properties:
RouteTableId: !Ref myRouteTable
DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0
GatewayId: !Ref myInternetGateway
mySubnetRouteTableAssociation:
Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation
Properties:
SubnetId: !Ref mySubnet
RouteTableId: !Ref myRouteTable
mySecurityGroup:
Type: AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup
Properties:
GroupDescription: Allow SSH and HTTP access
VpcId: !Ref myVPC
SecurityGroupIngress:
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 22
ToPort: 22
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
- IpProtocol: tcp
FromPort: 80
ToPort: 80
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
SecurityGroupEgress:
- IpProtocol: -1
FromPort: -1
ToPort: -1
CidrIp: 0.0.0.0/0
Tags:
- Key: stack
Value: production
myEC2Instance:
Type: AWS::EC2::Instance
Properties:
InstanceType: t2.micro
ImageId: ami-00a929b66ed6e0de6
SubnetId: !Ref mySubnet
SecurityGroupIds:
- !Ref mySecurityGroup
Tags:
- Key: Name
Value: MyEC2Instance
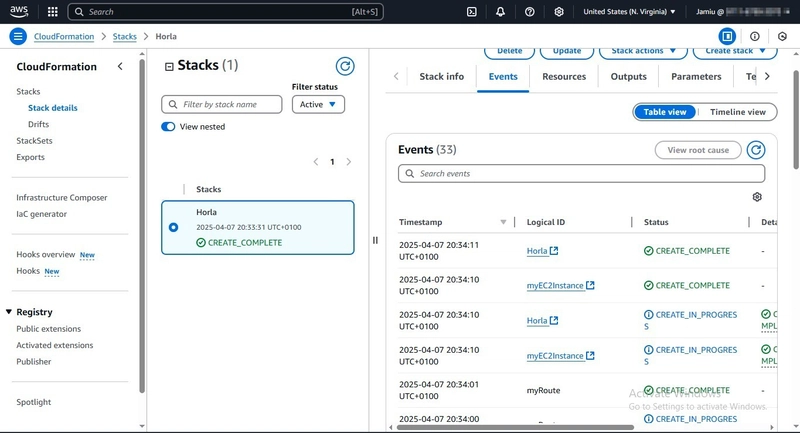
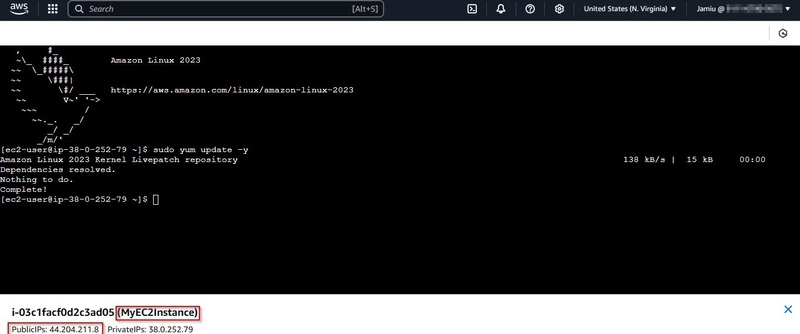
This snapshot shows; Deployment is completely created.
Deploying the Stack
- Save the template as
cloudformation-template.yml. - Use the AWS Management Console or CLI to deploy the stack:
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name MyStack --template-body file://cloudformation-template.yml
- Once deployed, you’ll see the resources in the Stack Resources tab of the CloudFormation console.
Snapshots of the Setup
- Table View: The CloudFormation console provides a detailed table view of all resources created by the stack, including their status and logical IDs.
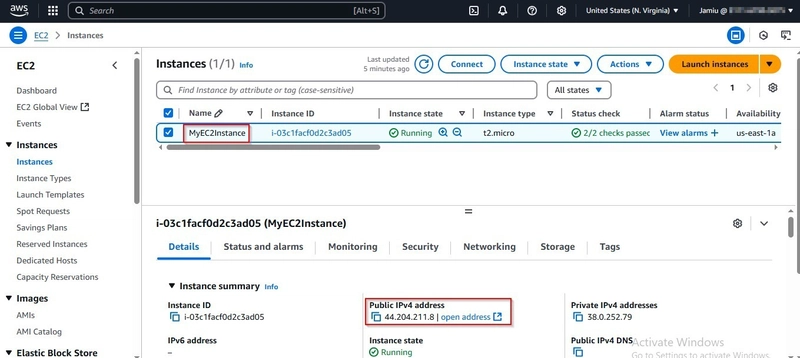
- EC2 Instance Running: After deployment, the EC2 instance will be running and accessible via SSH or HTTP, depending on the security group rules.
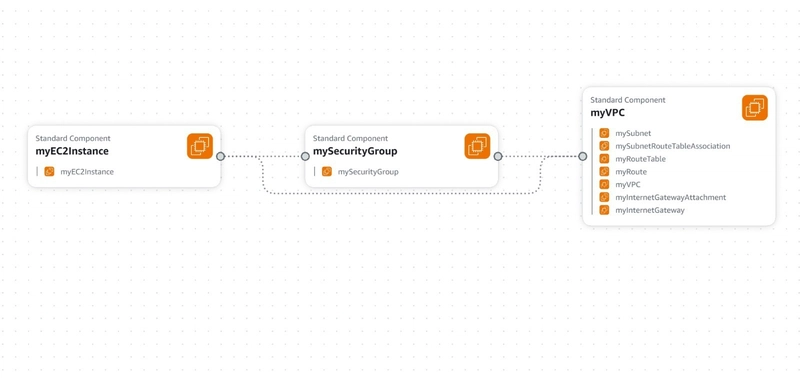
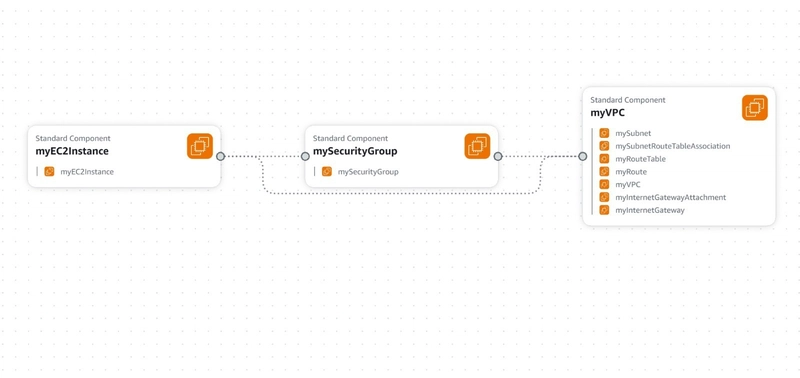
- Canva View: The CloudFormation Designer offers a visual representation of the stack, showing the relationships between resources.
Drift Detection
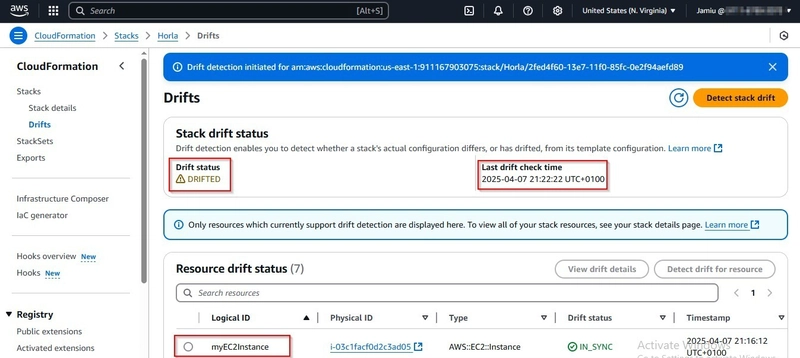
CloudFormation Drift Detection is a feature that identifies changes made to stack resources outside of CloudFormation. For example, When I manually deleted the EC2 instance, CloudFormation will detect the drift.
This is when I purposely terminated to know if it will be drifted as you can see the snapshot.
-
Trigger Drift Detection:
- Go to the CloudFormation console.
- Select the stack and click Drift Detection.
-
Drifted Signal:
- The EC2 instance is deleted, the stack will show a Drifted status.
- The drift report will highlight the missing EC2 instance.
This is when it drifted as you can see the snapshot.
Conclusion
AWS CloudFormation simplifies infrastructure management by allowing you to define resources as code. With features like drift detection, you can ensure your infrastructure remains consistent with your template. This setup is a great starting point for automating your AWS environment.
Feel free to share your thoughts or ask questions in the comments below! 😊







Top comments (0)