Introduction
Working with SQL databases in Node.js doesn't have to feel like writing a PhD thesis in raw SQL. In this guide, you'll learn how to build a simple but real-world Todo List App using modern tools: TypeScript, Drizzle ORM, and Neon DB.
Whether you're a beginner or looking to level up your backend workflow, this article will help you set up a type-safe, scalable, and serverless-ready SQL database using PostgreSQL without the usual headache.
What Is a Relational vs Non-Relational Database?
Before we dive into the tools, let's clarify two core types of databases:
Relational Database
A relational database organizes data into tables (rows and columns). These tables can be connected (or related) using keys like user_id. It's ideal when data consistency and structure are important.
Example (PostgreSQL Schema):
CREATE TABLE todos (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
task TEXT NOT NULL,
completed BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE
);
Non-Relational Database
A non-relational database (often called NoSQL) stores data in formats like documents (JSON), key-value pairs, or graphs. It's more flexible and scalable for unstructured or fast-changing data.
Example (MongoDB Document):
{
"_id": "1",
"task": "Buy milk",
"completed": false
}
🛠️ What Is an ORM?
ORM stands for Object-Relational Mapping. It's a tool that lets you write database queries using your application's language (like TypeScript), instead of raw SQL.
It helps with:
- Type safety
- Cleaner, more maintainable code
- Fewer bugs and less boilerplate
Without ORM:
INSERT INTO todos (task, user_id) VALUES ('Buy milk', 1);
With ORM (Drizzle):
await db.insert(todos).values({ task: "Buy milk", userId: 1 });
Meet Drizzle ORM
Drizzle ORM is a TypeScript-first ORM with:
- Strong typing
- Lightweight and fast
- Serverless-ready
- Familiar SQL-like syntax
As their docs put it, it's a "headless TypeScript ORM with a head" — meaning it gives you control without losing flexibility or dev experience.
What Is Neon DB?
Neon is a fully managed serverless PostgreSQL database designed for modern apps. It offers:
- Git-style branching for databases
- Auto-scaling serverless architecture
- Generous free tier
- Smooth integration with Drizzle and other tools
In short: it's PostgreSQL for the cloud-native era.
How Do Drizzle and Neon Work Together?
These two tools are made for each other:
- Neon hosts your cloud-based PostgreSQL database
- Drizzle connects to Neon using a connection string
- You write type-safe queries in Drizzle, and Neon runs them
Example setup:
import { neon } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/neon-http';
const sql = neon(process.env.DATABASE_URL!);
const db = drizzle(sql);
Example query:
await db.select().from(todos).where(eq(todos.userId, 1));
Getting Started
Let's begin by setting up our Node.js project.
Prerequisites
Make sure you have Node.js installed. If not, download it here.
Project Setup
Step 1: Create Project Folder
Create a folder and give it any name (we'll use todo-api-drizzle-neon):
mkdir todo-api-drizzle-neon
cd todo-api-drizzle-neon
Step 2: Initialize the Project
Run:
npm init -y
This will create a package.json file for you.
Step 3: Create the Source Folder
Inside your root folder, create a src folder. This is where your app logic will live.
Then create an index.ts file inside it:
todo-api-drizzle-neon/
└── src/
└── index.ts
Step 4: Install Dependencies
Install the required packages:
npm install express drizzle-kit drizzle-orm typescript @neondatabase/serverless dotenv
npm install --save-dev @types/express
Your package.json should now look like this:
{
"name": "todo-api-drizzle-neon",
"version": "1.0.0",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon src/index.ts",
"db:push": "drizzle-kit push",
"db:studio": "drizzle-kit studio",
"db:generate": "drizzle-kit generate",
"db:migrate": "tsx ./src/db/migrate.ts"
},
"dependencies": {
"@neondatabase/serverless": "^0.10.4",
"dotenv": "^16.5.0",
"drizzle-kit": "^0.31.1",
"drizzle-orm": "^0.44.1",
"express": "^5.1.0",
"typescript": "^5.8.3"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/express": "^5.0.2"
}
}
Step 5: Create a tsconfig.json File
Create a tsconfig.json file in your root directory:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"lib": ["es5", "es6"],
"target": "ES2018",
"module": "commonjs",
"moduleResolution": "node",
"rootDir": "./src",
"outDir": "dist",
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"sourceMap": true,
"esModuleInterop": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"typeRoots": ["./src/types", "./node_modules/@types"]
},
"include": ["src/**/*.ts"],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
Setting Up the Database
Step 1: Create a Neon Account
- Go to https://neon.tech and sign up for a free account
- Create a new project
- Copy your connection string from the dashboard
Step 2: Set Up Environment Variables
Create a .env file in your project root:
DATABASE_URL="your-neon-connection-string"
PORT=4000
Also, create a .gitignore file:
node_modules
.env
Step 3: Create Database Schema
Create src/db/schema.ts:
import { pgTable, serial, text, boolean } from 'drizzle-orm/pg-core';
export const todos = pgTable('todos', {
id: serial('id').primaryKey(),
task: text('task').notNull(),
completed: boolean('completed').default(false),
});
Step 4: Set Up Database Connection
Create src/db/index.ts:
import dotenv from 'dotenv';
dotenv.config();
import { neon } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import { drizzle } from 'drizzle-orm/neon-http';
import * as schema from './schema';
const sql = neon(process.env.DATABASE_URL!);
export const db = drizzle(sql, { schema });
Step 5: Configure Drizzle
Create drizzle.config.ts:
import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';
import { defineConfig } from 'drizzle-kit';
dotenv.config();
export default defineConfig({
schema: './src/db/schema.ts',
out: './drizzle',
dialect: 'postgresql',
dbCredentials: {
url: process.env.DATABASE_URL!
},
migrations: {
table: '__drizzle_migration',
schema: 'public'
},
verbose: true,
strict: true
});
Step 6: Push Schema to Database
Run:
npm run db:push
Implementing the Todo API
Now that our database is set up, let's create a RESTful API for managing todos.
Project Structure
src/
├── db/
│ ├── index.ts # Database connection
│ ├── schema.ts # Table definitions
│ └── migrate.ts # Migration script
├── routes/
│ └── todos.ts # Todo API endpoints
└── index.ts # Express app setup
Step 1: Create Express Server
Update src/index.ts:
import express from 'express';
import dotenv from 'dotenv';
import todoRoutes from './routes/todos';
dotenv.config();
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 4000;
// Middleware
app.use(express.json());
// Routes
app.use('/api/todos', todoRoutes);
// Health check endpoint
app.get('/health', (_req, res) => {
res.json({ status: 'ok' });
});
// Centralized error handling middleware
app.use((err: Error, _req: express.Request, res: express.Response, _next: express.NextFunction) => {
console.error(err.stack);
res.status(500).json({
error: 'Something went wrong!'
});
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`🚀 Server running at http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
Step 2: Implement Todo Routes
Create src/routes/todos.ts:
import { Router, RequestHandler } from 'express';
import { db } from '../db';
import { todos } from '../db/schema';
import { eq } from 'drizzle-orm';
const router = Router();
// Create a new todo
const createTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const { task } = req.body;
if (!task || typeof task !== 'string') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Task is required and must be a string'
});
return;
}
const [newTodo] = await db.insert(todos)
.values({ task })
.returning();
res.status(201).json(newTodo);
} catch (error) {
next(error); // Pass to error handling middleware
}
};
// Get all todos
const getAllTodos: RequestHandler = async (_req, res, next) => {
try {
const allTodos = await db.select().from(todos);
res.json(allTodos);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Get a single todo
const getTodoById: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
const [todo] = await db.select()
.from(todos)
.where(eq(todos.id, id));
if (!todo) {
res.status(404).json({
error: 'Todo not found'
});
return;
}
res.json(todo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Update a todo
const updateTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
const { task, completed } = req.body;
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
// Validate input
if (task !== undefined && typeof task !== 'string') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Task must be a string'
});
return;
}
if (completed !== undefined && typeof completed !== 'boolean') {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Completed must be a boolean'
});
return;
}
// Update todo
const [updatedTodo] = await db.update(todos)
.set({
...(task !== undefined && { task }),
...(completed !== undefined && { completed })
})
.where(eq(todos.id, id))
.returning();
if (!updatedTodo) {
res.status(404).json({
error: 'Todo not found'
});
return;
}
res.json(updatedTodo);
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Delete a todo
const deleteTodo: RequestHandler = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const id = parseInt(req.params.id);
if (isNaN(id)) {
res.status(400).json({
error: 'Invalid todo ID'
});
return;
}
await db.delete(todos)
.where(eq(todos.id, id));
res.status(204).send();
} catch (error) {
next(error);
}
};
// Register routes
router.post('/', createTodo);
router.get('/', getAllTodos);
router.get('/:id', getTodoById);
router.patch('/:id', updateTodo);
router.delete('/:id', deleteTodo);
export default router;
Step 3: Test the API
Start the server:
npm run dev
Test the endpoints using curl or Postman:
- Create a todo:
curl -X POST http://localhost:4000/api/todos \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"task": "Learn Drizzle ORM"}'
- Get all todos:
curl http://localhost:4000/api/todos
- Get a specific todo:
curl http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1
- Update a todo:
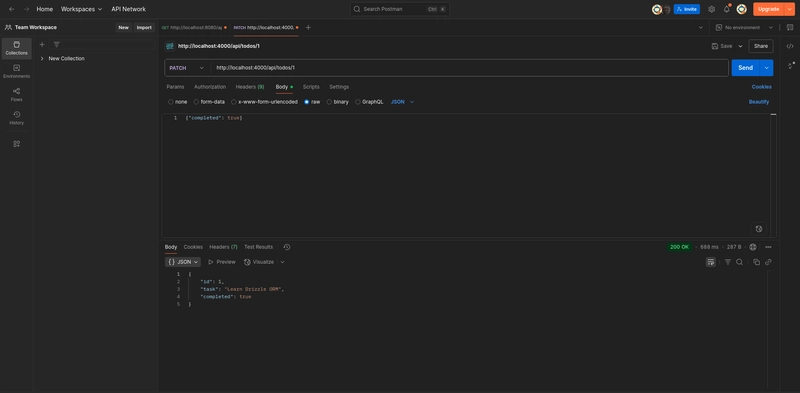
curl -X PATCH http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1 \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"completed": true}'
- Delete a todo:
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:4000/api/todos/1
Conclusion
In this guide, we've built a type-safe Todo API using:
- TypeScript for type safety
- Drizzle ORM for database operations
- Neon for serverless PostgreSQL
- Express for the API server
The result is a modern, scalable, and maintainable backend that's ready for production use. With TypeScript and Drizzle, we gain excellent type safety and developer experience. Neon gives us a cloud-native database that scales effortlessly.
If you found this article helpful, don’t forget to leave a like and drop a comment it really helps!
🔗 Stay connected:
Project Repository: View it on GitHub
Thanks for reading, and happy coding! 🚀









Top comments (2)
Nicee!!
I use Neon DB often, it’s a cool one! Will check out Drizzle
pretty cool, been through way messier setups before so seeing it mapped out like this is kinda satisfying. you think sticking with these tools long-term is mostly about habit or does tech just keep pulling you somewhere else every year?